The 21st century has brought to the forefront the power of data analytics (DA) and artificial intelligence (AI) as a means of improving health care around the globe.[1] As governments embark on data analytics and AI solutions, the question must be asked if the solution is able to deliver positive outcomes. This paper presents a solution that can be applied within a healthcare system and draws upon advanced Big Data analytics and Artificial Intelligence to influence patient prescription (drug) adherence [2] and leads to four key outcomes: [3,4]
- Increased drug adherence
- Improved patient outcomes
- Actionable data that supports disease management and research
- Improved cost efficiency through reduced waste.
Background
Medicines represent the first line of defence against illness and are one of our most cost-efficient health interventions. They improve our quality of life and, most critically, keep us alive. Despite a worldwide acknowledgment of the seriousness of the issue and efforts around the globe to improve medication adherence, there has been no significant change for the last 40+ years. The effectiveness of medicines, however, is predicated upon patients adhering to their prescribed medication(s) regimen. Non-adherence affects the patient’s health status, leading to unmanaged illness and a higher rate of avoidable, premature death.[5]
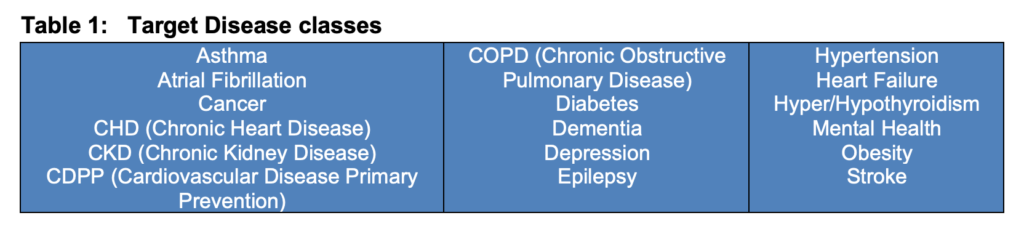
Below is a list of well-known chronic diseases that require medications to support a person’s health, well-being, quality of life, and life itself (Table 1). Hence, the impact of medication adherence on patient outcomes can not be under-estimated.
The economic and human costs are staggering as a result of drug non-adherence:
- More than 50 per cent of visits to a doctor, 40 percent of long-term care admissions and more than 50 per cent of hospital readmissions; [6]
- Is one of the key drivers to rising health care costs in Canada; [7]
- Cost of treating a patient with low adherence is twice that of a patient with high adherence; [9]
- It is estimated that as many as 40 to 70 per cent of Canadian patients are not taking their medications as directed by their physicians; the more severe the medical condition the less likely patients adhere. [18]
- Medication non-adherence is the source of an estimated $700 billion in “otherwise avoidable healthcare expenditure annually”; [11]
- Medication non-adherence is the 4th leading cause of death; [12]
Chronic disease and long-term illness account for 90 per cent of total healthcare expenditure;[13] over 50 per cent of total drug expenditure; [15] and escalating costs threaten drug program(s) sustainability. [14]
Benefits and implications
Below are key benefits that can be gained by adopting an AI-based healthcare solution: [18]
- Improved drug adherence – It has been shown that increases in adherence of between 30-37 per cent are very achievable.[19]
- Reduced healthcare costs – A 10 per cent improvement in medication adherence reduces healthcare costs by up to 29 per cent.[20]
- Faster time to treatment – With today’s huge patient caseloads, treating patients sooner saves both lives and healthcare costs.
- Big data analytics tools expedite the process by factoring in unique circumstances, such as adherence, lifestyle choices and demographics, along with the patient’s symptoms to help providers make more accurate diagnoses and to formulate the best treatment regimen in real-time.
- Reduced hospitalizations and readmissions – One of the best ways to curb healthcare costs is to keep patients from entering the hospital system in the first place.
- Risk stratification – A fully anonymized data helps track and identify the sickest and most at-risk, and often the costliest patients, in a proactive way.
- Improved medication therapy management –Big Data analytics helps clinicians and clinical pharmacists better co-manage drug therapies, all in real time – leading to better patient outcomes.
Methodology: An AI Approach
Any solution that seeks to address non-adherence needs to be scalable, dynamic, low cost and flexible.
The Curaizon™ solution, now available, is a patient-centric, interactive and technology-driven one. The strength of this solution is the real-time data reporting and advanced data analytics and AI techniques that provide valuable patient insights that empower medical professionals to be proactive rather than reactive.
Here’s how it works: Once patients are prescribed a medication, with the patient’s permission, the doctor enrolls them in CuraServe™. The enrollment enables the patients to receive reminders to take their medications, and when they do, they record it, which is captured in CuraData™. A unique feature of CuraServe™ is that it has a built-in safety net and can escalate non-adherence by notifying the patient’s family member or healthcare professional should the patient fail to take their medication. The healthcare provider, doctors and patients can see all their own records in CuraView™. It entails three major components described in Figure 1 below.
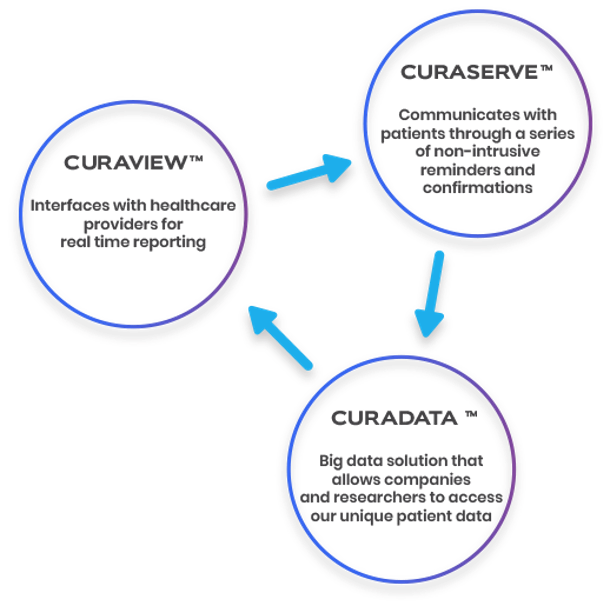
Figure 1: Relationship between Curaizon™ Components
A key feature of this Big Data and AI system is its ability to yield key indicators that can support contribution and attribution outcomes [2].
Conclusion
“If adherence therapy were a new drug, it would be hailed as a potentially major advance in medical treatment.” – Professor Richard Gray
There is no doubt that the spiralling costs of healthcare need to be checked and that finite resources must be used efficiently if we are to continue providing leading healthcare to the population while maintaining budgets.
By engaging with advanced data analytics and AI, healthcare providers can deliver scalable and cost-effective solutions that will dramatically improve patient outcomes, while reducing the avoidable waste that occurs as a result of low adherence to medications. The scale of the challenge before us is now matched by the technological advances necessary to affect real change.
References (make very small font)
- Glenn Monteith. (2018). Canada’s artificial-intelligence advantage in healthcare. Opinions. Downloaded from the internet on January 8, 2020. https://ipolitics.ca/2018/08/29/canadas-artificial-intelligence-advantage-in-healthcare/
- This paper defines adherence as: “The extent to which the patient’s behaviour matches agreed recommendations from the prescriber.”
- The AI solution focus herein leads to both contribution and attrition outcome management based on a theory of change.
- Curaizon™ does not guarantee and does not accept legal responsibility of any nature, for any indirect, special, incidental, consequential or other losses of any kind, in short, contract or otherwise (including but not limited to loss of revenue, income or profits, and loss of use or data), arising from or related to the accuracy, reliability, relevance or completeness of any material
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2019). Health and Economic Costs of Chronic Diseases. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/chronicdisease/about/costs/index.htm.
- Lau DT, Nau DP. (2004). Oral antihyperglycemic medication nonadherence and subsequent hospitalization among individuals with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 27(9): 2149-2153.
- Gupta, S. et al. (2018). Cost-related nonadherence to prescription medications in Canada: a scoping review. Dover Press, Patient Preference and Adherence. Volume 12, 16 May.
- Sequist, Thomas D , et al. (2005). A Randomized Trial of Electronic Clinical Reminders to Improve Quality of Care for Diabetes and Coronary Artery Disease .Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association, Volume 12, Issue 4, July, Pages 431–437, https://doi.org/10.1197/jamia.M1788.
- Montague, T.; Manness, Lori-Jean; Cochrane, Bonnie; Gogovor, Amédé ; Aylen, John; Martin, Lesli; and Nemis-White, Joanna. (2017). Non-adherence to Prescribed Therapy: A Persistent Contributor to the Care Gap. HCIC.
- This represents the number of patients in more than 40 countries covered by national health services around the globe.
- Kenneth, D.; Murphy, S.L.; Anderson, R.N.; and Scott C. (2002). National Vital Statistics Reports. Center for Disease Control: Division of Vital Statistics. Volume 53, Number 5.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2019). Health and Economic Costs of Chronic Diseases. Downloaded from the internet .https://www.cdc.gov/chronicdisease/about/costs/index.htm.
- Law, MR; et al (2012). The effect of cost on adherence to prescription medications in Canada. Canadian Medical Association Journal. 184(3): 297-302.
- Curaizon™ does not guarantee and does not accept legal responsibility of any nature, for any indirect, special, incidental, consequential or other losses of any kind, in short, contract or otherwise (including but not limited to loss of revenue, income or profits, and loss of use or data), arising from or related to the accuracy, reliability, relevance or completeness of any material
- Health Canada. (2019). A Prescription for Canada: Achieving Pharmacare for All. Final Report of the Advisory Council on the Implementation of National Pharmacare. ISBN: 978-0-660-30974-3
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2017). Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion. 28 June.
- Jeff, L. (2018). 5 Frightening Stats on Medication Adherence (plus Infographic). Philly Digest. May 16.
- IJ Staff (2019). Majority of Canadians do not take their medication as prescribed. Insurance Portal. April 30. Downloaded from the internet May 21, 2020. https://insurance-portal.ca/article/majority-of-canadians-do-not-take-their-medication-as-prescribed/
BIOs
Nicholas James Rumble
Nicholas is the founder and CEO of Curaizon and has a background in mathematics, economics and data. He has spent much of his working life inside investment banking, where he was instrumental in pioneering new trading technologies. He brings more than 20 years of business experience and knows how to bring teams of great people together and execute high-level plans; especially where technology plays a key role.
Betty Ann M. Turpin
Betty Ann, President of Turpin Consultants Inc., is a management consultant who has also worked in the federal government. Her career focus is performance measurement, data analytics, evaluation, and research. She is a Board Advisor on, and Canadian representative for, Curaizon.
Jack Bryant
Jack has spent his professional career in institutional sales and relationship management in the financial services and advertising industries in Boston and the San Francisco Bay Area. His passion is helping businesses efficiently grow while leveraging technology and key account management techniques.

